In long-term practice, we can realize that the establishment of a set of effective project and risk management mechanisms is crucial to improve the success rate of ERP system implementation. The planning, organization, management and monitoring of all aspects of the ERP project are to adopt internal and external continuous work procedures in order to achieve the expected results and goals after the project is implemented. This is the basic principle of balancing time, cost, and the need for product and service details that may conflict with each other.
The following is the introduction of the main content, tools and methods of ERP project management in combination with the actual experience of implementing ERP projects.
1.1 Typical project management cycle
A complete ERP project usually includes three phases: requirements analysis, system selection and system implementation; in the system implementation phase, it can be subdivided into five phases: implementation plan, business simulation testing, system development confirmation, system conversion operation, and post-operation evaluation. The main steps. Project management revolves around the entire process of the ERP project, and comprehensively manages and controls the project's project authorization, requirements analysis, software and hardware evaluation options, and system implementation. A typical ERP project management cycle usually includes: project start, project selection, project planning, project execution, project evaluation and update, and project completion.
1.1.1 Project start
Start The initial stage of the project mainly analyzes the needs, scope and feasibility of the ERP project, formulates the overall arrangement plan of the project, and determines the project responsibility and authorization by the enterprise and Fangtian in the form of "project contract". The project management at the beginning of the project mainly includes the following:
Needs assessment: Analyze and evaluate the company's overall needs and expectations, and make clear the expectations and goals of the ERP project results accordingly.
Project scope definition: Define the overall scope of the ERP project on the basis of clear corporate expectations and needs.
Feasibility analysis: According to the project's expectations and goals and the project's implementation scope, the company's own human resources, technical support and other aspects are evaluated, and the measures and investment resources needed to cooperate with the project are clearly identified.
overall General project arrangement: Make overall arrangements for the project's time, schedule, and personnel, and formulate the overall plan for the ERP project.
Project authorization: The enterprise signs an ERP project contract with Fangtian, clarifies the responsibilities of both parties, and the enterprise authorizes the other party to perform project management according to the needs of the project.
1.1.2 Project selection
明确 After clarifying the project's expectations and requirements, the main work of the system selection phase is to choose the appropriate software system and hardware platform for the enterprise. The general process of system selection is:
Screening of candidate suppliers: According to the expectations and needs of the enterprise, comprehensively analyze and evaluate the products of possible candidate software and hardware suppliers, and screen out several key candidates.
Candidate system demonstration: The key candidate will make targeted system demonstration to the management and relevant business departments of the enterprise according to the specific needs of the enterprise.
System evaluation and selection: According to the results of the demonstration, make a detailed analysis of the advantages and disadvantages of key candidates, and provide reference opinions to the company; The company determines the initial selection based on the results of the demonstration, and finally decides to be selected after business negotiations system.
The main project management work in the project selection phase is the risk control of system selection, including: correct and comprehensive evaluation of system functions, reasonable matching of system functions and own needs, comprehensive evaluation of supplier product functions and prices, technical support capabilities and other factors , And avoid bribery and fraud that may occur during the system selection process.
1.1.3 Project plan
The project planning phase is the start-up phase of the ERP project entering the system implementation. The main tasks include: determining the detailed project implementation scope, defining the submitted work results, assessing the main risks in the implementation process, formulating the time plan, cost and budget for project implementation. Planning, human resources planning, etc.
Determine the detailed project scope: Conduct business surveys and demand interviews with enterprises to understand the detailed needs of users, and formulate a system definition memorandum based on this to clarify the current status of users, specific needs and the detailed scope of system implementation.
Define the work results to be submitted: The enterprise and Fang Tian discuss and determine the work results that need to be submitted during the implementation of the system and at the end of the implementation, including the relevant implementation documents and the final online system.
Evaluate the main risks of implementation: Fangtian carries out a risk assessment of the implementation system based on the actual situation of the enterprise, and takes corresponding measures to prevent and control the estimated main risks.
Develop a time plan for the project: On the basis of determining the detailed project scope, defining the submitted work results, and clearly predicting the main risks, a detailed implementation time schedule is prepared according to the overall plan for system implementation.
Develop cost and budget plan: According to the overall cost and budget plan of the project, combined with the implementation time schedule, prepare specific system cost and budget control plans.
Develop human resources plan: determine the personnel arrangements during the implementation process, including Fangtian consultants and key business personnel on the enterprise side; for the key personnel involved in the implementation of the user, arrangements need to be made for their daily work to ensure the time for the implementation of the project Put in.
1.1.4 Project implementation
The project execution phase is the longest period in the implementation process, which runs through the three steps of business simulation test, system development confirmation and system conversion operation of the ERP project. The success of the implementation is related to the good or bad of the project management at this stage. The main contents of project management during the project implementation phase include:
Implementation of the implementation plan: carry out daily work according to the scheduled implementation plan, and timely solve various human resources, department coordination, personnel communication, technical support and other issues that occurred during the implementation process.
Control of time and cost: Control the time and cost of the project according to the actual progress of the implementation, and compare it with the plan, and take measures in time to exceed the time or cost plan.
Implementation documents: comprehensive documentation and management of the implementation process. Important documents need to be submitted to the project implementation leadership committee and all relevant implementation personnel.
Project progress report: In the form of a project progress report, all personnel who implement the project are regularly informed of the progress of the project implementation, the work that has been carried out and the issues that need to be further resolved.
例 Regular project meetings: Regularly hold project implementation meetings attended by enterprise project leaders, leaders of various business departments, and implementers to coordinate and resolve various issues during the implementation process.
Minutes of meetings: Prepare meeting minutes for all regular project meetings and symposiums, document and record the decisions made at the meeting or the results of the discussion, and distribute them to participants and relevant project implementers.
1.1.5 Project Evaluation and Update
of The core of the project evaluation and update phase is project monitoring, which is to use project management tools and technologies to measure and update project tasks. Project evaluation and update also run through the three steps of business simulation test, system development confirmation and system conversion operation of the ERP project. The project management tools and techniques commonly used in the project evaluation and update stages are:
Phased evaluation: conduct a phased evaluation of the project implementation, and summarize whether the implementation is on schedule and achieve the expected phased results. If there are deviations, study whether the plan and resources need to be updated, and implement the required update measures.
里程碑 Project milestone meeting: When the project reaches an important milestone stage, a project milestone meeting is held to summarize the work of the previous stage and evaluate the implementation progress and results, and mobilize the deployment of the work of the next stage.
Quality assurance system: Through training and knowledge transfer to the user personnel involved in the implementation, writing and perfecting various documents during the implementation process, thereby establishing a quality assurance system to ensure that after the implementation is completed, the enterprise can achieve a complete grasp of the system and continuous improvement The goal.
1.1.6 Project completion
The project completion stage is the last stage of the entire implementation project. At this point, the work is nearing completion and the project implementation results have been achieved. At this final stage, there are still important project management tasks to be carried out. Don't take it lightly:
Administrative acceptance: In combination with the project's initial expectations and goals for the system, inspect the project implementation results.
Project summary: Review and summarize the project implementation process and implementation results.
Experience exchange: exchange and share experiences and lessons in the implementation process.
Formal transfer: The system is officially operated and used, and the computer department of the enterprise performs routine maintenance and technical support.
The work throughout the above six project management stages is: project performance measurement and quality management, and project risk management control.
1.2 Project performance measurement standards and quality management
Quality management is one of the important aspects of project management. Establishing and implementing appropriate performance measurement standards is the key to project quality management.
1.2.1 Establish project performance metrics
依据 The basis for formulating the project performance measurement standards is the project plan. The project expectations are established through the specific content of the project objectives and implementation strategies as the basis and core of the project performance measurement standards. Specific project performance measures can include the following main content:
Work scope and project specific steps;
Basic time estimation and cost budget;
Financial forecasts and funding plans;
详细 detailed work arrangements;
Quality requirements;
满意 Satisfaction of the project team;
满意 end-user satisfaction;
满意 Satisfaction level of the management and the investor.
1.2.2 Observe the actual performance of the project
正式 Collect relevant information about project implementation through formal or informal channels during project implementation and observe the actual performance of the project. The information pipelines available in this step are:
Formal channels, such as: project progress reports, regular project meetings, project milestone meetings, various meeting minutes, etc .;
Informal channels, such as: conversations and discussions with project team members or end users, informal communication with corporate management or funders, etc.
1.2.3 Compare actual performance and metrics
Compare the actual performance of the project implementation with the pre-established measurement standards, mainly by answering two questions: "How is the project progressing?" And "If there is a deviation from the project plan, how did it happen?"
Performance measurement standards provide a basis for objective evaluation of the project status, so that decision makers can make an objective and fair judgment on the actual progress of the project quickly and effectively, so as to take necessary measures in a timely manner. It is always the responsibility of the project team and the company's senior management to evaluate the progress of the project through performance measures.
1.2.4 Take corrective action
比较 After comparing the actual performance of the project with the measurement standards, if deviations occur, corrective measures need to be taken to bring the implementation project back on track in a timely manner. Corrective actions can take the following forms:
Rework the project plan;
Rearrange project steps;
Reallocate project resources;
Adjust project organization and project management methods.
1.3 Management and control of project risks
In the practical experience of enterprises implementing ERP systems, we realized that the potential risks of ERP projects include: software risks-such as software function risks and software selection risks; implementation risks-such as project organization risks, time and schedule control risks, Cost control risk and implementation quality control risk; transformation risk—risk of changing management concepts, risk of organizational structure adjustment, risk of changing performance evaluation system, etc. The management and control of various risks that occur or may occur during the ERP project process is an important part of project management throughout the entire process of the ERP project.
The following is an introduction to the aspects and tools of project risk management and control.
1.3.1 Risk management model
For the risk management of an ERP implementation project, first of all, it is necessary to have a deep understanding and understanding of the project itself, and to understand the project to identify various potential risks by understanding the project. Based on the identification of project risks, assess the control points for project risk management. After identifying the project risk and testing the control points of risk management, screening and identifying the remaining project risks that need to be focused on, and further explaining the remaining risks in this part. In the process of project implementation, special measures are taken to manage and control this part of the risk, so as to minimize the risk and control the risk.
In the above risk management model, it can be found that in the initial understanding of the project, there may be a large number of potential risks identified; after assessing the control points of project risk management, the potential risks are screened, and those that can be applied using common project management measures Potential risks to avoid and overcome, so that implementers can focus on those few remaining risks; after the remaining risks are determined, the corresponding management and control are targeted, so that the overall risk of implementation can be effectively achieved control.
It can be seen that the essence of risk management is: identifying risks, screening risks, controlling key risks, and ultimately reducing risks.
1.3.2 Specific content of risk management
Usually risk management can be divided into four steps: identifying risks, measuring risks, managing risks, and monitoring project performance.
The main task of identifying risks is to identify the risks that may affect the implementation of the project and record the characteristics of the risks. It should be noted that: risk identification runs through the entire process of project implementation, not just the beginning of the project; possible risks include various internal and external factors; while identifying risks, it is necessary to dialectically analyze their negatives Effects (ie, threats posed by risks) and positive effects (ie, potential opportunities).
Measuring risks is mainly to evaluate the identified risks, determine the interaction between risks and risks, and a series of potential consequences. At the same time, it is necessary to determine the importance of risks and the priority order for dealing with risks. The analysis tools available at this stage include tools such as "risk assessment matrix", "expected return on investment", "simulation" and "decision tree".
Managing risk is the most direct and critical step in risk control. In the process of risk management, it is necessary to formulate enhancement measures for the positive effects of risks (that is, potential opportunities) and methods for coping with the negative effects of risks (that is, possible threats). For different risks, corresponding measures need to be taken to control according to their importance, impact magnitude, and determined processing priorities. The response to negative risks can be avoided, minimized or managed to accept. In addition, when dealing with risks, it is necessary to pay attention to "timeliness"-that is, to make judgments and take measures against various sudden risks at the first time; and "repetitive"-that is, to risks that have occurred or have been controlled Frequent reviews are needed to ensure that risks can be controlled in a stable and long-term manner.
Finally, we need to monitor the project process, check the actual effect of risk control, and evaluate the overall performance of the project.
In summary, project management is to control the project from different aspects such as performance measurement and quality management, risk management control through the project management cycle, so that the enterprise can achieve the expected results and goals of the project. Project management plays a vital role in the successful implementation of ERP projects and the management and control of various implementation risks.
1.4 Guidelines for System Construction
According to Fang Tian's long-term experience in the development and implementation of enterprise management information system software, the following basic guiding principles for building an enterprise information management system are summarized:
Responsible person in charge, efficiency-driven, overall planning, key breakthroughs, step-by-step implementation, promotion and application.
The person in charge is in charge: it is the leadership guarantee that the project can be successfully implemented. The introduction of a computer management system by an enterprise will involve changes in the management of the entire enterprise, and in the process of application, it will face certain business process adjustments and mobilization of personnel, equipment, funds and other resources, coordination of the work of various functional departments, and even corporate organization Restructuring of the architecture. Therefore, there must be a strong core of leadership to lead, support, direct, care and coordinate the entire project. This is a prerequisite for successful project implementation.
Benefit-driven: The implementation of the system is to improve business management, to win the market, and to maximize the benefits. Therefore, the entire project should define an overall goal: the implementation of the ERP system is to further improve the efficiency of the enterprise.
Overall planning: As the computer application of enterprise management involves all aspects of enterprise management, in order to ensure the reliable operation of the entire system and achieve seamless connection between various modules, the overall planning of the project must be made, which is also the fundamental guarantee for the success of the project.
Key breakthroughs and step-by-step implementation: The company's most urgent needs are targeted for key breakthroughs, which are effective quickly; step-by-step implementation is to diversify investment and reduce investment risks.
Promotion and application: ERP management ideas permeate the management of data information inside and outside the enterprise. Fangtian ERP system software strictly follows the principles of ERP, the various modules of the system, and the data of each department are an organic combination of integrated design. The more widely the system is implemented inside the enterprise, the more it can reflect the superiority of system integration, and the more it can play the management benefits of ERP.
1.5 Project Management
1.5.1 Leading Group
The implementation of ERP system must not only invest a considerable amount of capital, but more importantly, the enterprise must invest a lot of manpower and material resources. The key to project implementation lies in the people. Improper selection will directly affect the cycle, benefits and success of the project.
overall The overall structure of project management is shown in the figure below:
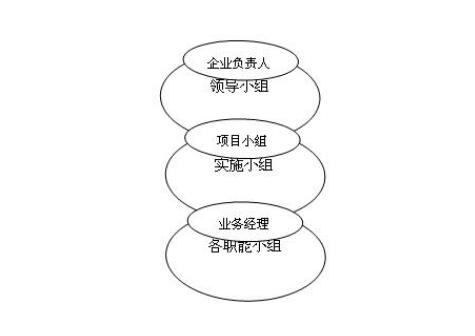
Since the application of the computer management system in the enterprise will involve changes in the management of the entire enterprise, it is recommended that the first person in charge of the enterprise be the team leader, including the business vice president, project manager, and general manager (or deputy general manager) Fang Tian. Leading group.
The main contents of his work are:
of The mobilization of project implementation calls on all employees of the enterprise to actively participate in and cooperate with the project implementation.
The deployment of human resources, the appointment of project managers, and the establishment of relevant reward and punishment systems.
Establish the quality and cost awareness of employees, promote team spirit, and shape corporate culture.
Dare to reform and rectify, have the firm intention of project implementation, dare to change the management system that is not in line with market competition, do not cooperate with the rectification work, and sacrifice the collective interest for personal interests.
Guide and coordinate project implementation and determine target benefits.
1.5.2 Implementation Team
The project implementation team is responsible for Fangtian's ERP system implementation planning, which plays a role in supporting the whole project. The project manager is usually the leader of the implementation team. This is a very important position. Therefore, the requirements for the project manager are as follows:
Must be very familiar with the situation of the enterprise, and have relatively comprehensive corporate management experience.
I must have some prestige, be able to coordinate the relationship between various departments, and be able to accept new ideas and concepts faster.
I should have a certain understanding of computer systems.
Have a high cultural quality, be good at expression, persuade people with reason, and be able to work together with others.
Can quickly master Fangtian ERP system and understand its design ideas.
Once confirmed by the project manager, it should not be changed easily.
Other team members are composed of system analysts who are familiar with internal management and computer systems, managers of various functional departments, and Fang Tian implementation consultants. Its main functions are:
Develop an implementation plan to ensure that the plan is realized;
Organize, direct and promote the work of functional groups;
Responsible for data preparation, monitoring the accuracy and completeness of the input data;
Responsible for system testing and navigation, study the differences between Fangtian ERP system and current management, and propose solutions and suggestions;
Develop training plans and carry out internal training;
Preside over the formulation of new working standards and procedures;
Submit reports on the work results of each stage;
The daily maintenance work of Fangtian ERP system ensures the normal operation of the system.
1.5.3 Functional Group
The members of the functional group mainly include the leaders or business backbones of the company's production and manufacturing departments and related functional departments, such as planning, production, engineering, materials, procurement, finance, and sales departments. The team members should be very familiar with the work and situation of the department, and also understand the situation and interrelationships of other departments, and be dedicated and enterprising, and can quickly accept new things and understand the new management model.
main The main responsibilities of the functional group are:
Organize the basic data of each functional department, such as: material code, structure list, process code, job unit price, inventory information, etc .;
Specify and combine the system to determine the work process of each functional department;
Implement Fangtian's ERP system design ideas to each employee in each department;
During the system trial operation, feedback the system's executive layer information, and study and solve the problems in management.



